# fdsan使用指导
## 1. 功能介ç»
fdsan针对的æ“作对象是文件æ述符,主è¦ç”¨äºŽæ£€æµ‹ä¸åŒä½¿ç”¨è€…对相åŒæ–‡ä»¶æ述符的错误æ“作,包括多次关é—(double-close)和关é—åŽä½¿ç”¨ï¼ˆuse-after-close)。这些文件æ述符å¯ä»¥æ˜¯æ“作系统ä¸çš„文件ã€ç›®å½•ã€ç½‘络套接å—和其他I/O设备ç‰ï¼Œåœ¨ç¨‹åºä¸ï¼Œæ‰“开文件或套接å—会生æˆä¸€ä¸ªæ–‡ä»¶æ述符,如果æ¤æ–‡ä»¶æ述符在使用åŽå‡ºçŽ°åå¤å…³é—ã€æˆ–者关é—åŽä½¿ç”¨ç‰åœºæ™¯ï¼Œå°±ä¼šé€ æˆå†…å˜æ³„露ã€æ–‡ä»¶å¥æŸ„泄露ç‰å®‰å…¨éšæ‚£é—®é¢˜ã€‚该类问题éžå¸¸éšè”½ï¼Œä¸”难以排查,为了更好地检测æ¤ç±»é—®é¢˜ï¼Œå› æ¤å¼•å…¥äº†æ¤ç§é’ˆå¯¹æ–‡ä»¶æ述符错误æ“作的检测工具fdsan。
## 2. 实现原ç†
设计æ€è·¯ï¼šå½“打开已有文件或创建一个新文件的时候,在得到返回fdåŽï¼Œè®¾ç½®ä¸€ä¸ªå…³è”çš„tag,æ¥æ ‡è®°fd的属主信æ¯ï¼›å…³é—文件å‰ï¼Œæ£€æµ‹fdå…³è”çš„tag,判æ–是å¦ç¬¦åˆé¢„期(属主信æ¯ä¸€è‡´),符åˆå°±ç»§ç»èµ°æ£å¸¸æ–‡ä»¶å…³é—æµç¨‹ï¼›å¦‚æžœä¸ç¬¦åˆå°±æ˜¯æ£€æµ‹åˆ°å¼‚å¸¸ï¼Œæ ¹æ®è®¾ç½®ï¼Œè°ƒç”¨å¯¹åº”的异常处ç†ã€‚
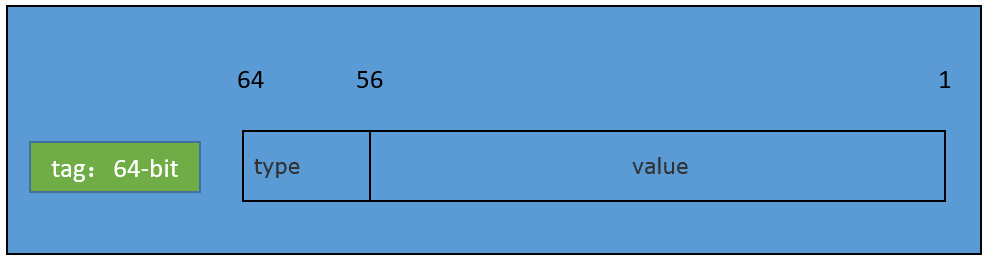
tag由两部分组æˆï¼Œæœ€é«˜ä½çš„8-bitæž„æˆtype,åŽé¢çš„56-bitæž„æˆvalue。
typeï¼Œæ ‡è¯†fd通过何ç§å°è£…å½¢å¼è¿›è¡Œç®¡ç†ï¼Œä¾‹å¦‚ `FDSAN_OWNER_TYPE_FILE`就表示fd通过普通文件进行管ç†ï¼Œtype类型在 `fdsan_owner_type`进行定义。
valueï¼Œåˆ™ç”¨äºŽæ ‡è¯†å®žé™…çš„owner tag。
tagæž„æˆå›¾ç¤º
## 3. 接å£è¯´æ˜Ž
### fdsan_set_error_level
```
enum fdsan_error_level fdsan_set_error_level(enum fdsan_error_level new_level);
```
**æ述:** å¯ä»¥é€šè¿‡`fdsan_set_error_level`设定error_level,error_level用于控制检测到异常åŽçš„处ç†è¡Œä¸ºã€‚默认error_level为FDSAN_ERROR_LEVEL_WARN_ALWAYS。
**å‚数:** fdsan_error_level
| å称 | 说明 |
| -------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
| `FDSAN_ERROR_LEVEL_DISABLED` | disabled,æ¤level代表什么都ä¸å¤„ç†ã€‚ |
| `FDSAN_ERROR_LEVEL_WARN_ONCE` | warn-once,第一次出现错误时在hilogä¸å‘出è¦å‘Šï¼Œç„¶åŽå°†çº§åˆ«é™ä½Žä¸ºdisabled(FDSAN_ERROR_LEVEL_DISABLED)。 |
| `FDSAN_ERROR_LEVEL_WARN_ALWAYS` | warn-always,æ¯æ¬¡å‡ºçŽ°é”™è¯¯æ—¶éƒ½åœ¨hilogä¸å‘出è¦å‘Šã€‚ |
| `FDSAN_ERROR_LEVEL_FATAL` | fatal,出现错误时调用abort异常退出。 |
**返回值:** 返回旧的error_level。
### fdsan_get_error_level
```
enum fdsan_error_level fdsan_get_error_level();
```
**æ述:** å¯ä»¥é€šè¿‡`fdsan_get_error_level`获å–error level。
**返回值:** 当å‰çš„error_level。
### fdsan_create_owner_tag
```
uint64_t fdsan_create_owner_tag(enum fdsan_owner_type type, uint64_t tag);
```
**æ述:** é€šè¿‡ä¼ å…¥çš„typeå’Œtagå—段,拼接æˆä¸€ä¸ªæœ‰æ•ˆçš„文件æ述符的关é—tag。
**å‚数:** fdsan_owner_type
| å称 | 说明 |
| -------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
| `FDSAN_OWNER_TYPE_GENERIC_00` | 默认未使用fd对应的type值 |
| `FDSAN_OWNER_TYPE_GENERIC_FF` | 默认éžæ³•fd对应的type值 |
| `FDSAN_OWNER_TYPE_FILE` | 默认普通文件对应的type值,使用fopen或fdopen打开的文件具有该类型 |
| `FDSAN_OWNER_TYPE_DIRECTORY` | 默认文件夹对应的type值,使用opendir或fdopendir打开的文件具有该类型 |
| `FDSAN_OWNER_TYPE_UNIQUE_FD` | 默认unique_fd对应的type值,ä¿ç•™æš‚未使用 |
| `FDSAN_OWNER_TYPE_ZIPARCHIVE` | 默认zip压缩文件对应的type值,ä¿ç•™æš‚未使用 |
**返回值:** 返回创建的tag,å¯ä»¥ç”¨äºŽfdsan_exchange_owner_tag函数的输入。
### fdsan_exchange_owner_tag
```
void fdsan_exchange_owner_tag(int fd, uint64_t expected_tag, uint64_t new_tag);
```
**æ述:** 修改文件æ述符的关é—tag。
通过fd所以找到对应的FdEntry,判æ–close_tag值与expected_tag是å¦ä¸€è‡´ï¼Œä¸€è‡´è¯´æ˜Žç¬¦åˆé¢„期,å¯ä»¥ç”¨new_tag值é‡æ–°è®¾å®šå¯¹åº”çš„FdEntry。
如果ä¸ç¬¦åˆï¼Œåˆ™è¯´æ˜Žæ£€æµ‹åˆ°äº†å¼‚常,åŽç»åˆ™è¿›è¡Œå¯¹åº”的异常处ç†ã€‚
**å‚数:**
| å称 | 类型 | 说明 |
| -------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
| `fd` | int | fdå¥æŸ„,作为FdEntry的索引 |
| `expected_tag` | uint64_t | 期望的ownership tag值 |
| `new_tag` | uint64_t | 设置新的ownership tag值 |
### fdsan_close_with_tag
```
int fdsan_close_with_tag(int fd, uint64_t tag);
```
**æ述:** æ ¹æ®tagæ述符关é—文件æ述符。
通过fd找到匹é…çš„FdEntry。如果close_tag与tag相åŒï¼Œåˆ™ç¬¦åˆé¢„期,å¯ä»¥ç»§ç»æ‰§è¡Œæ–‡ä»¶æ述符关é—æµç¨‹ï¼Œå¦åˆ™æ„味ç€æ£€æµ‹åˆ°å¼‚常。
**å‚数:**
| å称 | 类型 | 说明 |
| -------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
| `fd` | int | å¾…å…³é—çš„fdå¥æŸ„ |
| `tag` | uint64_t | 期望的ownership tag |
**返回值:** 0或者-1,0表示closeæˆåŠŸï¼Œ-1表示close失败。
### fdsan_get_owner_tag
```
uint64_t fdsan_get_owner_tag(int fd);
```
**æ述:** æ ¹æ®æ–‡ä»¶æ述符获å–tagä¿¡æ¯ã€‚
通过fd找到匹é…çš„FdEntry,并获å–其对应的close_tag。
**å‚数:**
| å称 | 类型 | 说明 |
| -------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
| `tag` | uint64_t | ownership tag |
**返回值:** 返回对应fd的tag。
### fdsan_get_tag_type
```
const char* fdsan_get_tag_type(uint64_t tag);
```
**æ述:** æ ¹æ®tag计算出对应的type类型。
通过获å–到的tagä¿¡æ¯ï¼Œé€šè¿‡è®¡ç®—获å–对应tagä¸çš„typeä¿¡æ¯ã€‚
**å‚数:**
| å称 | 类型 | 说明 |
| -------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
| `tag` | uint64_t | ownership tag |
**返回值:** 返回对应tag的type。
### fdsan_get_tag_value
```
uint64_t fdsan_get_tag_value(uint64_t tag);
```
**æ述:** æ ¹æ®tag计算出对应的owner value。
通过获å–到的tagä¿¡æ¯ï¼Œé€šè¿‡å移计算获å–对应tagä¸çš„valueä¿¡æ¯ã€‚
**å‚数:**
| å称 | 类型 | 说明 |
| -------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------ |
| `tag` | uint64_t | ownership tag |
**返回值:** 返回对应tag的value。
## 4. 使用示例
如何使用fdsan?这是一个简å•çš„double-close问题:
```
void good_write()
{
sleep(1);
int fd = open(DEV_NULL_FILE, O_RDONLY);
sleep(3);
ssize_t ret = write(fd, "fdsan test\n", 11);
if (ret == -1) {
OH_LOG_ERROR(LOG_APP, "good write but failed?!");
}
close(fd);
}
void bad_close()
{
int fd = open(DEV_NULL_FILE, O_RDONLY);
close(fd);
sleep(2);
// This close expected to be detect by fdsan
close(fd);
}
void functional_test()
{
std::vector<std::thread> threads;
for (auto function : { good_write, bad_close }) {
threads.emplace_back(function);
}
for (auto& thread : threads) {
thread.join();
}
}
int main()
{
functional_test();
return 0;
}
```
上述代ç ä¸çš„`good_write`函数会打开一个文件并写入一些å—符串而`bad_close`函数ä¸ä¹Ÿä¼šæ‰“开一个文件åŒæ—¶åŒ…å«double-close问题,这两个线程åŒæ—¶è¿è¡Œé‚£ä¹ˆç¨‹åºçš„æ‰§è¡Œæƒ…å†µä¼šæ˜¯è¿™æ ·çš„ã€‚
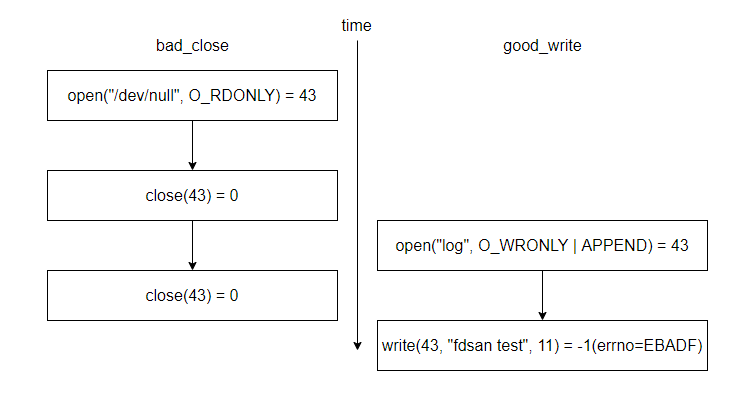
由于æ¯æ¬¡open返回的fd是顺åºåˆ†é…的,在进入主函数åŽç¬¬ä¸€ä¸ªå¯ç”¨çš„fd是43,`bad_close`函数ä¸ç¬¬ä¸€æ¬¡open返回的fd是43,在关é—之åŽï¼Œ43å°±å˜æˆäº†å¯ç”¨çš„fd,在`good_write`函数ä¸open返回了第一个å¯ç”¨çš„fd,å³43,但是由于`bad_close`函数ä¸å˜åœ¨double-closeé—®é¢˜ï¼Œå› æ¤é”™è¯¯çš„å…³é—了å¦ä¸€ä¸ªçº¿ç¨‹ä¸æ‰“开的文件,导致写入失败。
在fdsan引入之åŽï¼Œæœ‰ä¸¤ç§æ–¹æ³•å¯ä»¥æ£€æµ‹è¿™ç±»é—®é¢˜ï¼šä½¿ç”¨æ ‡å‡†åº“接å£æˆ–实现具有fdsan的函数接å£ã€‚
### ä½¿ç”¨æ ‡å‡†åº“æŽ¥å£
æ ‡å‡†åº“æŽ¥å£ä¸fopen,fdopen,opendir,fdopendir都已ç»é›†æˆäº†fdsan,使用å‰è¿°æŽ¥å£è€Œéžç›´æŽ¥ä½¿ç”¨openå¯ä»¥å¸®åŠ©æ£€æµ‹é—®é¢˜ã€‚在å‰è¿°æ¡ˆä¾‹ä¸å¯ä»¥ä½¿ç”¨fopen替代open:
```c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define TEMP_FILE "/data/local/tmp/test.txt"
void good_write()
{
// fopen is protected by fdsan, replace open with fopen
// int fd = open(TEMP_FILE, O_RDONLY);
FILE *f = fopen(TEMP_FILE, "w+");
if (f == NULL) {
printf("fopen failed errno=%d\n", errno);
return;
}
// ssize_t ret = write(fd, "fdsan test\n", 11);
int ret = fprintf(f, "fdsan test %d\n", 11);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("fprintf failed errno=%d\n", errno);
}
// close(fd);
fclose(f);
}
```
使用fopen打开的æ¯ä¸ªæ–‡ä»¶æ述符都需è¦æœ‰ä¸€ä¸ªä¸Žä¹‹å¯¹åº”çš„ `tag` 。`fdsan` 在 `close` 时会检查关é—çš„ `fd` 是å¦ä¸Ž `tag` 匹é…,ä¸åŒ¹é…就会默认æ示相关日志信æ¯ã€‚下é¢æ˜¯ä¸Šè¿°ä»£ç 的日志信æ¯ï¼š
```
# hilog | grep MUSL-FDSAN
04-30 15:03:41.760 10933 1624 E C03f00/MUSL-FDSAN: attempted to close file descriptor 43, expected to be unowned, actually owned by FILE* 0x00000000f7b90aa2
```
从这里的错误信æ¯ä¸å¯ä»¥çœ‹å‡ºFILE接å£ä½“的文件被其他人错误的关é—了,FILE接å£ä½“的地å€å¯ä»¥å助进一æ¥å®šä½ã€‚
æ¤å¤–,å¯ä»¥åœ¨ä»£ç ä¸ä½¿ç”¨`fdsan_set_error_level`设置错误ç‰çº§error_level,设置为Fatal之åŽå¦‚æžœfdsan检测到错误会æ示日志信æ¯åŒæ—¶crash生æˆå †æ ˆä¿¡æ¯ç”¨äºŽå®šä½ã€‚下é¢æ˜¯error_level设置为Fatal之åŽç”Ÿæˆçš„crashå †æ ˆä¿¡æ¯ï¼š
```
Reason:Signal:SIGABRT(SI_TKILL)@0x0000076e from:1902:20010043
Fault thread info:
Tid:15312, Name:e.myapplication
#00 pc 000e65bc /system/lib/ld-musl-arm.so.1(raise+176)(3de40c79448a2bbced06997e583ef614)
#01 pc 0009c3bc /system/lib/ld-musl-arm.so.1(abort+16)(3de40c79448a2bbced06997e583ef614)
#02 pc 0009de4c /system/lib/ld-musl-arm.so.1(fdsan_error+116)(3de40c79448a2bbced06997e583ef614)
#03 pc 0009e2e8 /system/lib/ld-musl-arm.so.1(fdsan_close_with_tag+836)(3de40c79448a2bbced06997e583ef614)
#04 pc 0009e56c /system/lib/ld-musl-arm.so.1(close+20)(3de40c79448a2bbced06997e583ef614)
#05 pc 000055d8 /data/storage/el1/bundle/libs/arm/libentry.so(bad_close()+96)(f3339aac824c099f449153e92718e1b56f80b2ba)
#06 pc 00006cf4 /data/storage/el1/bundle/libs/arm/libentry.so(decltype(std::declval<void (*)()>()()) std::__n1::__invoke[abi:v15004]<void (*)()>(void (*&&)())+24)(f3339aac824c099f449153e92718e1b56f80b2ba)
#07 pc 00006c94 /data/storage/el1/bundle/libs/arm/libentry.so(f3339aac824c099f449153e92718e1b56f80b2ba)
#08 pc 000067b8 /data/storage/el1/bundle/libs/arm/libentry.so(void* std::__n1::__thread_proxy[abi:v15004]<std::__n1::tuple<std::__n1::unique_ptr<std::__n1::__thread_struct, std::__n1::default_delete<std::__n1::__thread_struct>>, void (*)()>>(void*)+100)(f3339aac824c099f449153e92718e1b56f80b2ba)
#09 pc 00105a6c /system/lib/ld-musl-arm.so.1(start+248)(3de40c79448a2bbced06997e583ef614)
#10 pc 000700b0 /system/lib/ld-musl-arm.so.1(3de40c79448a2bbced06997e583ef614)
```
æ¤æ—¶ï¼Œä»Žcrashä¿¡æ¯ä¸å¯ä»¥çœ‹åˆ°æ˜¯bad_closeä¸å˜åœ¨é—®é¢˜ï¼ŒåŒæ—¶crashä¸ä¹ŸåŒ…å«äº†æ‰€æœ‰æ‰“开的文件,å助进行定ä½ï¼Œæå‡æ•ˆçŽ‡ã€‚
```
OpenFiles:
0->/dev/null native object of unknown type 0
1->/dev/null native object of unknown type 0
2->/dev/null native object of unknown type 0
3->socket:[28102] native object of unknown type 0
4->socket:[28103] native object of unknown type 0
5->anon_inode:[eventpoll] native object of unknown type 0
6->/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace_marker native object of unknown type 0
7->anon_inode:[eventpoll] native object of unknown type 0
8->anon_inode:[eventpoll] native object of unknown type 0
9->/dev/console native object of unknown type 0
10->pipe:[95598] native object of unknown type 0
11->pipe:[95598] native object of unknown type 0
12->socket:[18542] native object of unknown type 0
13->pipe:[96594] native object of unknown type 0
14->socket:[18545] native object of unknown type 0
15->pipe:[96594] native object of unknown type 0
16->anon_inode:[eventfd] native object of unknown type 0
17->/dev/binder native object of unknown type 0
18->/data/storage/el1/bundle/entry.hap native object of unknown type 0
19->anon_inode:[eventpoll] native object of unknown type 0
20->anon_inode:[signalfd] native object of unknown type 0
21->socket:[29603] native object of unknown type 0
22->anon_inode:[eventfd] native object of unknown type 0
23->anon_inode:[eventpoll] native object of unknown type 0
24->anon_inode:[eventfd] native object of unknown type 0
25->anon_inode:[eventpoll] native object of unknown type 0
26->anon_inode:[eventfd] native object of unknown type 0
27->anon_inode:[eventpoll] native object of unknown type 0
28->anon_inode:[eventfd] native object of unknown type 0
29->anon_inode:[eventpoll] native object of unknown type 0
30->anon_inode:[eventfd] native object of unknown type 0
31->anon_inode:[eventpoll] native object of unknown type 0
32->anon_inode:[eventfd] native object of unknown type 0
33->anon_inode:[eventpoll] native object of unknown type 0
34->anon_inode:[eventfd] native object of unknown type 0
35->socket:[97409] native object of unknown type 0
36->socket:[94716] native object of unknown type 0
38->socket:[94720] native object of unknown type 0
40->/data/storage/el1/bundle/entry_test.hap native object of unknown type 0
41->socket:[95617] native object of unknown type 0
42->/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace_marker native object of unknown type 0
43->/dev/null FILE* 4155724704
44->socket:[94737] native object of unknown type 0
45->pipe:[95634] native object of unknown type 0
46->pipe:[95634] native object of unknown type 0
47->pipe:[95635] native object of unknown type 0
49->pipe:[95636] native object of unknown type 0
50->pipe:[95636] native object of unknown type 0
```
### 实现具有fdsan的函数接å£
除了直接使用具有fdsanåŠŸèƒ½çš„æ ‡å‡†åº“å‡½æ•°ä¹‹å¤–ï¼Œè¿˜å¯ä»¥å®žçŽ°å…·æœ‰fdsan的函数接å£ã€‚fdsan机制主è¦é€šè¿‡ä¸¤ä¸ªæŽ¥å£å®žçŽ°ï¼š`fdsan_exchange_owner_tag`å’Œ`fdsan_close_with_tag`,fdsan_exchange_owner_tagå¯ä»¥è®¾ç½®å¯¹åº”fdçš„tag,而fdsan_close_with_tagå¯ä»¥åœ¨å…³é—文件时检查对应的tag是å¦æ£ç¡®ã€‚
下é¢æ˜¯ä¸€ä¸ªå…·æœ‰fdsan的函数接å£å®žçŽ°å®žä¾‹ï¼š
```cpp
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <utility>
struct fdsan_fd {
fdsan_fd() = default;
explicit fdsan_fd(int fd)
{
reset(fd);
}
fdsan_fd(const fdsan_fd& copy) = delete;
fdsan_fd(fdsan_fd&& move)
{
*this = std::move(move);
}
~fdsan_fd()
{
reset();
}
fdsan_fd& operator=(const fdsan_fd& copy) = delete;
fdsan_fd& operator=(fdsan_fd&& move)
{
if (this == &move) {
return *this;
}
reset();
if (move.fd_ != -1) {
fd_ = move.fd_;
move.fd_ = -1;
// Acquire ownership from the moved-from object.
exchange_tag(fd_, move.tag(), tag());
}
return *this;
}
int get()
{
return fd_;
}
void reset(int new_fd = -1)
{
if (fd_ != -1) {
close(fd_, tag());
fd_ = -1;
}
if (new_fd != -1) {
fd_ = new_fd;
// Acquire ownership of the presumably unowned fd.
exchange_tag(fd_, 0, tag());
}
}
private:
int fd_ = -1;
// Use the address of object as the file tag
uint64_t tag()
{
return reinterpret_cast<uint64_t>(this);
}
static void exchange_tag(int fd, uint64_t old_tag, uint64_t new_tag)
{
if (&fdsan_exchange_owner_tag) {
fdsan_exchange_owner_tag(fd, old_tag, new_tag);
}
}
static int close(int fd, uint64_t tag)
{
if (&fdsan_close_with_tag) {
return fdsan_close_with_tag(fd, tag);
}
}
};
```
这里的实现ä¸ä½¿ç”¨`fdsan_exchange_owner_tag`在开始时将fd与结构体对象地å€ç»‘定,然åŽåœ¨å…³é—文件时使用`fdsan_close_with_tag`进行检测,预期tag是结构体对象地å€ã€‚
在实现了具有fdsan的函数接å£ä¹‹åŽï¼Œå¯ä»¥ä½¿ç”¨è¯¥æŽ¥å£åŒ…装fd:
```cpp
#define TEMP_FILE "/data/local/tmp/test.txt"
void good_write()
{
// int fd = open(DEV_NULL_FILE, O_RDONLY);
fdsan_fd fd(open(TEMP_FILE, O_CREAT | O_RDWR));
if (fd.get() == -1) {
printf("fopen failed errno=%d\n", errno);
return;
}
ssize_t ret = write(fd.get(), "fdsan test\n", 11);
if (ret == -1) {
printf("write failed errno=%d\n", errno);
}
fd.reset();
}
```
æ¤æ—¶è¿è¡Œè¯¥ç¨‹åºå¯ä»¥æ£€æµ‹åˆ°å¦ä¸€ä¸ªçº¿ç¨‹çš„double-close问题,详细信æ¯å¯ä»¥å‚考3.2节。åŒæ ·ä¹Ÿå¯ä»¥è®¾ç½®error_level为fatalï¼Œè¿™æ ·å¯ä»¥ä½¿fdsan在检测到crash之åŽä¸»åŠ¨crash以获å–更多信æ¯ã€‚