# RelativeContainer
相对布局组件,用于复杂场景中元素对齐的布局。
> **说明:**
>
> 该组件从API Version 9开始支持。后续版本如有新增内容,则采用上角标单独标记该内容的起始版本。
## 规则说明
* 容器内子组件区分水平方向,垂直方向:
* 水平方向为left, middle, right,对应容器的HorizontalAlign.Start, HorizontalAlign.Center, HorizontalAlign.End。
* 垂直方向为top, center, bottom,对应容器的VerticalAlign.Top, VerticalAlign.Center, VerticalAlign.Bottom。
* 子组件可以将容器、guideline、barrier或者其他子组件设为锚点:
* 参与相对布局的容器内组件,不设置id的组件能显示,但是不能被其他子组件作为锚点,相对布局容器会为其拼接id,此id的规律无法被应用感知;容器id固定为__container__;guideline和barrier的id不能与组件重复,重复的话按照组件 > guideline > barrier的优先级生效。
* 此子组件某一方向上的三个位置(水平方向为left、middle、right,垂直方向为top、center、bottom)可以指定容器或其他子组件同方向的三个位置(水平方向为HorizontalAlign.Start、HorizontalAlign.Center、HorizontalAlign.End,垂直方向为VerticalAlign.Top、VerticalAlign.Center、VerticalAlign.Bottom)为锚点。若同方向上设置两个以上锚点,水平方向Start和Center优先,垂直方向Top和Center优先。例如,水平方向上指定了left以容器的HorizontalAlign.Start为锚点,middle以容器的HorizontalAlign.Center为锚点,又指定right的锚点为容器的HorizontalAlign.End,当组件的width和容器的width不能同时满足3条约束规则时,优先取Start和Center的约束规则。
* 当同时存在前端页面设置的子组件尺寸和相对布局规则时,子组件的绘制尺寸取决于约束规则。从API Version 11开始,该规则发生变化,子组件绘制尺寸取决于前端页面设置的尺寸。
* 对齐后需要额外偏移可设置offset(API Version 11上新增了[bias](ts-universal-attributes-location.md#bias对象说明), 不建议再使用offset)。
* 从API Version 11开始,在RelativeContainer组件中,width、height设置auto表示自适应子组件。
* 当width设置auto时,如果水平方向上子组件以容器作为锚点,则auto不生效,垂直方向上同理。
* 相对布局容器内的子组件的margin含义不同于通用属性的margin,其含义为到该方向上的锚点的距离。若该方向上没有锚点,则该方向的margin不生效。
* guideline的位置在不声明或者声明异常值(如undefined)时,取start:0的位置;start和end两种方式声明一种即可,同时声明时仅start生效。
* 当容器在某个方向的size声明为“auto”时,该方向上guideline的位置只能使用start的方式声明(不可使用百分比)。
* 垂直方向的guideline和barrier只能作为组件水平方向的锚点,作为垂直方向的锚点时取0;水平方向的guideline和barrier只能作为组件垂直方向的锚点,作为水平方向的锚点时取0。
* 链的形成依靠组件间的依赖关系。以一个组件A、组件B组成的最小水平链为例,需要有锚点1 <-- 组件A <---> 组件B --> 锚点2的依赖关系,即A具有left锚点,B具有right锚点,同时A的right锚点是B的HorizontalAlign.Start,B的left锚点是A的HorizontalAlign.End。
* 链的方向和格式声明在链头组件的[chainMode](ts-universal-attributes-location.md#chainmode12)接口;链内元素的bias属性全部失效,链头元素的bias作为整个链的bias生效。
* 链内所有元素的size如果超出链的锚点约束,超出的部分将均分在链的两侧。在[Packed](ts-universal-attributes-location.md#chainstyle12)链中,超出部分的分布可以通过[bias](ts-universal-attributes-location.md#bias对象说明)来设置。
* 特殊情况
* 根据约束条件和子组件本身的size属性无法确定子组件大小,则子组件不绘制。
* 互相依赖、环形依赖时容器内子组件全部不绘制。
* 同方向上两个及以上位置设置锚点但锚点位置逆序时此子组件大小为0,即不绘制。
## 子组件
支持多个子组件。
## 接口
RelativeContainer()
**卡片能力:** 从API version 9开始,该接口支持在ArkTS卡片中使用。
**原子化服务API:** 从API version 11开始,该接口支持在原子化服务中使用。
**系统能力:** SystemCapability.ArkUI.ArkUI.Full
## 属性
除支持[通用属性](ts-universal-attributes-size.md)外,还支持如下属性:
### guideLine12+
guideLine(value: Array<GuideLineStyle>)
设置RelativeContainer容器内的辅助线,Array中每个项目即为一条guideline。
**原子化服务API:** 从API version 12开始,该接口支持在原子化服务中使用。
**系统能力:** SystemCapability.ArkUI.ArkUI.Full
**参数:**
| 参数名 | 类型 | 必填 | 说明 |
| ------ | ------------------------------------------ | ---- | --------------------------------- |
| value | Array<[GuideLineStyle](#guidelinestyle12对象说明)> | 是 | RelativeContainer容器内的辅助线。 |
### barrier12+
barrier(value: Array<BarrierStyle>)
设置RelativeContainer容器内的屏障,Array中每个项目即为一条barrier。
**原子化服务API:** 从API version 12开始,该接口支持在原子化服务中使用。
**系统能力:** SystemCapability.ArkUI.ArkUI.Full
**参数:**
| 参数名 | 类型 | 必填 | 说明 |
| ------ | -------------------------------------- | ---- | ------------------------------- |
| value | Array<[BarrierStyle](#barrierstyle12对象说明)> | 是 | RelativeContainer容器内的屏障。 |
### barrier12+
barrier(barrierStyle: Array<LocalizedBarrierStyle>)
设置RelativeContaine容器内的屏障,Array中每个项目即为一条barrier。
**原子化服务API:** 从API version 12开始,该接口支持在原子化服务中使用。
**系统能力:** SystemCapability.ArkUI.ArkUI.Full
**参数:**
| 参数名 | 类型 | 必填 | 说明 |
| ------ | -------------------------------------- | ---- | ------------------------------ |
| barrierStyle | Array\<[LocalizedBarrierStyle](#localizedbarrierstyle12对象说明)\> | 是 | RelativeContaine容器内的屏障。 |
## GuideLineStyle12+对象说明
guideLine参数,用于定义一条guideline的id、方向和位置。
**原子化服务API:** 从API version 12开始,该接口支持在原子化服务中使用。
**系统能力:** SystemCapability.ArkUI.ArkUI.Full
| 名称 | 类型 | 必填 | 说明 |
| ----- | ------- | ---- | --------------------- |
| id | string | 是 | guideline的id,必须是唯一的并且不可与容器内组件重名。 |
| direction | [Axis](ts-appendix-enums.md#axis) | 是 | 指定guideline的方向。
默认值:Axis.Vertical |
| position | [GuideLinePosition](#guidelineposition12对象说明) | 是 | 指定guideline的位置。
默认值:
{
start: 0
} |
## GuideLinePosition12+对象说明
guideLine位置参数,用于定义guideline的位置。
**原子化服务API:** 从API version 12开始,该接口支持在原子化服务中使用。
**系统能力:** SystemCapability.ArkUI.ArkUI.Full
| 名称 | 类型 | 必填 | 说明 |
| ----- | ------- | ---- | --------------------- |
| start | [Dimension](ts-types.md#dimension10) | 否 | guideline距离容器左侧或者顶部的距离。 |
| end | [Dimension](ts-types.md#dimension10) | 否 | guideline距离容器右侧或者底部的距离。 |
## BarrierStyle12+对象说明
barrier参数,用于定义一条barrier的id、方向和生成时所依赖的组件。
**原子化服务API:** 从API version 12开始,该接口支持在原子化服务中使用。
**系统能力:** SystemCapability.ArkUI.ArkUI.Full
| 名称 | 类型 | 必填 | 说明 |
| ----- | ------- | ---- | --------------------- |
| id | string | 是 | barrier的id,必须是唯一的并且不可与容器内组件重名。 |
| direction | [BarrierDirection](ts-container-relativecontainer.md#barrierdirection12) | 是 | 指定barrier的方向。
默认值:BarrierDirection.LEFT |
| referencedId | Array\ | 是 | 指定生成barrier所依赖的组件。 |
## BarrierDirection12+枚举说明
定义屏障线的方向。
**原子化服务API:** 从API version 12开始,该接口支持在原子化服务中使用。
**系统能力:** SystemCapability.ArkUI.ArkUI.Full
| 名称 | 说明 |
| ------ | ----------------------------- |
| LEFT | 屏障在其所有[referencedId](ts-container-relativecontainer.md#barrierstyle12对象说明)的最左侧。 |
| RIGHT | 屏障在其所有[referencedId](ts-container-relativecontainer.md#barrierstyle12对象说明)的最右侧。 |
| TOP | 屏障在其所有[referencedId](ts-container-relativecontainer.md#barrierstyle12对象说明)的最上方。 |
| BOTTOM | 屏障在其所有[referencedId](ts-container-relativecontainer.md#barrierstyle12对象说明)的最下方。 |
## LocalizedBarrierStyle12+对象说明
barrier参数,用于定义一条barrier的id、方向和生成时所依赖的组件。
**原子化服务API:** 从API version 12开始,该接口支持在原子化服务中使用。
**系统能力:** SystemCapability.ArkUI.ArkUI.Full
| 名称 | 类型 | 必填 | 说明 |
| ----- | ------- | ---- | --------------------- |
| id | string | 是 | barrier的id,必须是唯一的并且不可与容器内组件重名。 |
| localizedDirection | [LocalizedBarrierDirection](#localizedbarrierdirection12枚举说明) | 是 | 指定barrier的方向。 |
| referencedId | Array\ | 是 | 指定生成barrier所依赖的组件。 |
## LocalizedBarrierDirection12+枚举说明
定义屏障线的方向。
**原子化服务API:** 从API version 12开始,该接口支持在原子化服务中使用。
**系统能力:** SystemCapability.ArkUI.ArkUI.Full
| 名称 | 值 | 说明 |
| ------ | -- | ----------------------------- |
| START | 0 |屏障在其所有[referencedId](#localizedbarrierstyle12对象说明)的最左/右侧,LTR模式时为最左侧,RTL模式时为最右侧。 |
| END | 1 | 屏障在其所有[referencedId](#localizedbarrierstyle12对象说明)的最左/右侧, LTR模式时为最右侧,RTL模式时为最左侧。 |
| TOP | 2 | 屏障在其所有[referencedId](#localizedbarrierstyle12对象说明)的最上方。 |
| BOTTOM | 3 | 屏障在其所有[referencedId](#localizedbarrierstyle12对象说明)的最下方。 |
## 示例
### 示例1(以容器和容器内组件作为锚点进行布局)
本示例通过alignRules接口实现了以容器和容器内组件作为锚点进行布局的功能。
```ts
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Row() {
RelativeContainer() {
Row() {
Text('row1')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#a3cf62')
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: "__container__", align: VerticalAlign.Top },
left: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.Start }
})
.id("row1")
Row() {
Text('row2')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#00ae9d')
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: "__container__", align: VerticalAlign.Top },
right: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.End }
})
.id("row2")
Row() {
Text('row3')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#0a59f7')
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: "row1", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom },
left: { anchor: "row1", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
right: { anchor: "row2", align: HorizontalAlign.Start }
})
.id("row3")
Row() {
Text('row4')
}.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.backgroundColor('#2ca9e0')
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: "row3", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom },
bottom: { anchor: "__container__", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom },
left: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
right: { anchor: "row1", align: HorizontalAlign.End }
})
.id("row4")
Row() {
Text('row5')
}.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.backgroundColor('#30c9f7')
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: "row3", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom },
bottom: { anchor: "__container__", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom },
left: { anchor: "row2", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
right: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.End }
})
.id("row5")
}
.width(300).height(300)
.margin({ left: 50 })
.border({ width: 2, color: "#6699FF" })
}
.height('100%')
}
}
```

### 示例2(子组件设置外边距)
本示例展示了容器内子组件设置外边距的用法。
```ts
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Row() {
RelativeContainer() {
Row() {
Text('row1')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#a3cf62')
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: "__container__", align: VerticalAlign.Top },
left: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.Start }
})
.id("row1")
.margin(10)
Row() {
Text('row2')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#00ae9d')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "row1", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: { anchor: "row1", align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
.id("row2")
Row() {
Text('row3')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#0a59f7')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "row1", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
top: { anchor: "row1", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
.id("row3")
Row() {
Text('row4')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#2ca9e0')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "row3", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: { anchor: "row2", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
.id("row4")
.margin(10)
}
.width(300).height(300)
.margin({ left: 50 })
.border({ width: 2, color: "#6699FF" })
}
.height('100%')
}
}
```

### 示例3(设置容器大小自适应内容)
本示例展示了容器大小适应内容(声明width或height为"auto")的用法。
```ts
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Row() {
RelativeContainer() {
Row() {
Text('row1')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#a3cf62')
.id("row1")
Row() {
Text('row2')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#00ae9d')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "row1", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: { anchor: "row1", align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
.id("row2")
Row() {
Text('row3')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#0a59f7')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "row1", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
top: { anchor: "row1", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
.id("row3")
Row() {
Text('row4')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#2ca9e0')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "row3", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: { anchor: "row2", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
.id("row4")
}
.width("auto").height("auto")
.margin({ left: 50 })
.border({ width: 2, color: "#6699FF" })
}
.height('100%')
}
}
```
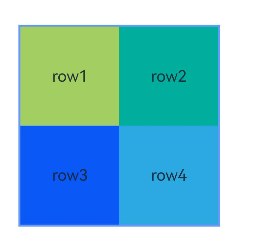
### 示例4(设置偏移)
本示例通过[bias](ts-universal-attributes-location.md#bias对象说明)实现了子组件的位置在竖直方向的两个锚点间偏移的效果
```ts
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Row() {
RelativeContainer() {
Row()
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#a3cf62')
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: "__container__", align: VerticalAlign.Top },
bottom: { anchor: "__container__", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom },
left: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
right: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
bias: { vertical: 0.3 }
})
.id("row1")
}
.width(300).height(300)
.margin({ left: 50 })
.border({ width: 2, color: "#6699FF" })
}
.height('100%')
}
}
```

### 示例5(设置辅助线)
本示例展示了相对布局组件通过[guideLine](#guideline12)接口设置辅助线,子组件以辅助线为锚点的功能。
```ts
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Row() {
RelativeContainer() {
Row()
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#a3cf62')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "guideline1", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: { anchor: "guideline2", align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
.id("row1")
}
.width(300)
.height(300)
.margin({ left: 50 })
.border({ width: 2, color: "#6699FF" })
.guideLine([{ id: "guideline1", direction: Axis.Vertical, position: { start: 50 } },
{ id: "guideline2", direction: Axis.Horizontal, position: { start: 50 } }])
}
.height('100%')
}
}
```
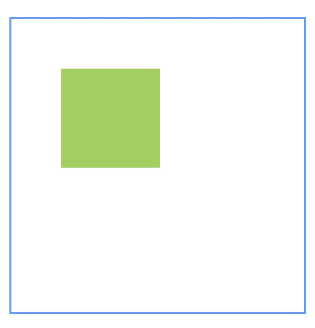
### 示例6(设置屏障)
本示例展示了相对布局组件通过[barrier](#barrier12)接口设置屏障,子组件以屏障为锚点的用法。
```ts
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Row() {
RelativeContainer() {
Row() {
Text('row1')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#a3cf62')
.id("row1")
Row() {
Text('row2')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#00ae9d')
.alignRules({
middle: { anchor: "row1", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: { anchor: "row1", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
.id("row2")
Row() {
Text('row3')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#0a59f7')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "barrier1", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: { anchor: "row1", align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
.id("row3")
Row() {
Text('row4')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(50)
.height(50)
.backgroundColor('#2ca9e0')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "row1", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
top: { anchor: "barrier2", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
.id("row4")
}
.width(300)
.height(300)
.margin({ left: 50 })
.border({ width: 2, color: "#6699FF" })
.barrier([{ id: "barrier1", direction: BarrierDirection.RIGHT, referencedId: ["row1", "row2"] },
{ id: "barrier2", direction: BarrierDirection.BOTTOM, referencedId: ["row1", "row2"] }])
}
.height('100%')
}
}
```

### 示例7(设置链)
本示例通过[chainMode](ts-universal-attributes-location.md#chainmode12)接口从上至下分别实现了水平方向的[SPREAD链,SPREAD_INSIDE链和PACKED链](ts-universal-attributes-location.md#chainstyle12)。
```ts
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Row() {
RelativeContainer() {
Row() {
Text('row1')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(80)
.height(80)
.backgroundColor('#a3cf62')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
right: { anchor: "row2", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
top: { anchor: "__container__", align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
.id("row1")
.chainMode(Axis.Horizontal, ChainStyle.SPREAD)
Row() {
Text('row2')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(80)
.height(80)
.backgroundColor('#00ae9d')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "row1", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
right: { anchor: "row3", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
top: { anchor: "row1", align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
.id("row2")
Row() {
Text('row3')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(80)
.height(80)
.backgroundColor('#0a59f7')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "row2", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
right: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: { anchor: "row1", align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
.id("row3")
Row() {
Text('row4')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(80)
.height(80)
.backgroundColor('#a3cf62')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
right: { anchor: "row5", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
center: { anchor: "__container__", align: VerticalAlign.Center }
})
.id("row4")
.chainMode(Axis.Horizontal, ChainStyle.SPREAD_INSIDE)
Row() {
Text('row5')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(80)
.height(80)
.backgroundColor('#00ae9d')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "row4", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
right: { anchor: "row6", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
top: { anchor: "row4", align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
.id("row5")
Row() {
Text('row6')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(80)
.height(80)
.backgroundColor('#0a59f7')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "row5", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
right: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: { anchor: "row4", align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
.id("row6")
Row() {
Text('row7')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(80)
.height(80)
.backgroundColor('#a3cf62')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
right: { anchor: "row8", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
bottom: { anchor: "__container__", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
.id("row7")
.chainMode(Axis.Horizontal, ChainStyle.PACKED)
Row() {
Text('row8')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(80)
.height(80)
.backgroundColor('#00ae9d')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "row7", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
right: { anchor: "row9", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
top: { anchor: "row7", align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
.id("row8")
Row() {
Text('row9')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(80)
.height(80)
.backgroundColor('#0a59f7')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "row8", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
right: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: { anchor: "row7", align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
.id("row9")
}
.width(300).height(300)
.margin({ left: 50 })
.border({ width: 2, color: "#6699FF" })
}
.height('100%')
}
}
```

### 示例8(链中设置偏移)
本示例通过[chainMode](ts-universal-attributes-location.md#chainmode12)和[bias](ts-universal-attributes-location.md#bias对象说明)接口实现了水平方向的带偏移的[PACKED链](ts-universal-attributes-location.md#chainstyle12)。
```ts
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Row() {
RelativeContainer() {
Row() {
Text('row1')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(80)
.height(80)
.backgroundColor('#a3cf62')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
right: { anchor: "row2", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
center: { anchor: "__container__", align: VerticalAlign.Center },
bias: { horizontal: 0 }
})
.id("row1")
.chainMode(Axis.Horizontal, ChainStyle.PACKED)
Row() {
Text('row2')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(80)
.height(80)
.backgroundColor('#00ae9d')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "row1", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
right: { anchor: "row3", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
top: { anchor: "row1", align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
.id("row2")
Row() {
Text('row3')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(80)
.height(80)
.backgroundColor('#0a59f7')
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: "row2", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
right: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: { anchor: "row1", align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
.id("row3")
}
.width(300).height(300)
.margin({ left: 50 })
.border({ width: 2, color: "#6699FF" })
}
.height('100%')
}
}
```

### 示例9(设置镜像模式)
本示例展示了在镜像模式(direction声明Direction.Rtl)下以屏障为锚点时使用[LocalizedAlignRuleOptions](ts-universal-attributes-location.md#localizedalignruleoptions12对象说明)和[LocalizedBarrierDirection](#localizedbarrierdirection12枚举说明)设置对齐方式的用法。
```ts
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
Row() {
RelativeContainer() {
Row() {
Text('row1')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#a3cf62')
.id("row1")
Row() {
Text('row2')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#00ae9d')
.alignRules({
middle: { anchor: "row1", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: { anchor: "row1", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
.id("row2")
Row() {
Text('row3')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#0a59f7')
.alignRules({
start: { anchor: "barrier1", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: { anchor: "row1", align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
.id("row3")
Row() {
Text('row4')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(50)
.height(50)
.backgroundColor('#2ca9e0')
.alignRules({
start: { anchor: "row1", align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
top: { anchor: "barrier2", align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
.id("row4")
}
.direction(Direction.Rtl)
.width(300)
.height(300)
.margin({ left: 50 })
.border({ width: 2, color: "#6699FF" })
.barrier([{ id: "barrier1", localizedDirection: LocalizedBarrierDirection.END, referencedId: ["row1", "row2"] },
{ id: "barrier2", localizedDirection: LocalizedBarrierDirection.BOTTOM, referencedId: ["row1", "row2"] }])
}
.height('100%')
}
}
```
